Tracking medical products on Fantom
According to the World Health Organization, 10% of the medical products in low- and middle-income countries are substandard or counterfeit.
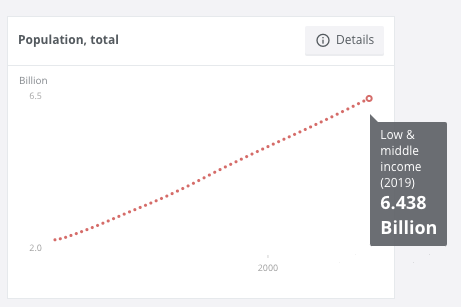
Currently 85% percent of the total world population, or 6.438 billion people, are living in low-income and middle-income countries.
While low- and middle-income countries are more exposed to falsified drugs, the issue affects every country in the world.
Clandestine manufacturing facilities are relatively easy and quick to assemble, and the global economy's expansion facilitates distribution across different countries in the global markets.
What are the consequences of counterfeit medical products?
Counterfeit medicines represent an enormous threat to people’s health. As reported in the study, these drugs:
- May cause harm to patients and fail to treat the diseases for which they were intended.
- Lead to loss of confidence in medicines, healthcare providers, and health systems.
- Contribute to antimicrobial resistance and drug-resistant infections.
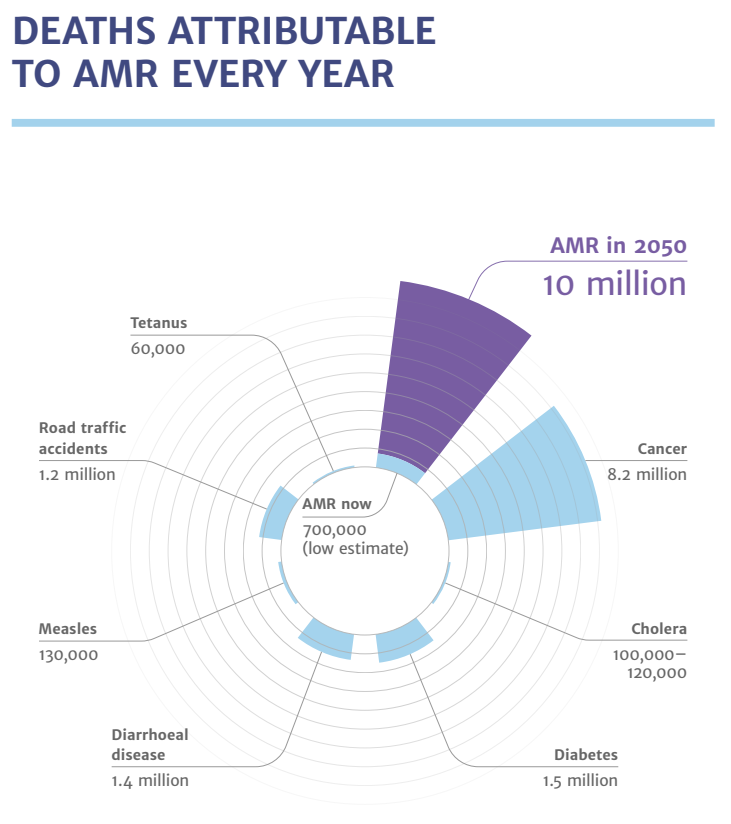
According to the Review of Antimicrobial Resistance, commissioned in July 2014 by the UK Prime Minister, the currently estimated deaths caused by antimicrobial resistance is 700,000 per year.
It is forecasted that by 2050, antimicrobial resistance will kill up to 10 million people per year.
Classification of counterfeit medical products
The World Health Organization separates counterfeit drugs into three categories:
- Falsified medical products that deliberately and fraudulently misrepresent their identity, composition, and source.
- Substandard medical products that fail to meet quality standards.
- Unregistered or unlicensed medical products that have not been evaluated or approved.
How do I identify a counterfeit medical product?
Identifying a falsified drug is hard. Clandestine manufacturers are constantly refining their products, and some are visually identical to their genuine counterparts.
The patient can perform a packaging inspection and look for errors and discrepancies against the genuine drug. They can also inspect the product itself, and look for visual or olfactive anomalies. Lastly, they can discuss with their doctor or pharmacist if they suspect that the product is counterfeit.
Unfortunately, these measures are not effective. They put the burden of verifying the authenticity onto the patient, adding a layer of complexity and discomfort to their already unpleasant disease or illness the drug is supposed to cure.
Additionally, the patients, mostly living in low- and middle-income countries, might not have the means to perform the check themselves.
Blockchain for tracking of medical products
At Fantom, we put our technology at work and launched a pilot program commissioned by the Ministry of Health of Afghanistan, and in partnership with global pharmaceutical producers Bliss GVS and Nabros Pharma, and medical products distributor Royal Star.
Pharmaceutical producers and distributors will store several data points on-chain. Patients and healthcare providers will be able to verify the authenticity of a drug by using the Chekkit app.
With the app, checking a medical product is as simple as scanning a QR code with your phone.
Fantom’s blockchain provides a layer of security and trust, independent from any third party. The blockchain is immutable and always accessible by anyone anywhere in the world, guaranteeing an unparalleled level of transparency.
How does the supply-chain tracking work?
The process is simple:
- The pharmaceutical producers will apply trackable labels to the medicines.
- The distributors will scan these labels at each step of the distribution process. Each scan will generate a cryptographic seal of the data–called hash– that will be timestamped and saved on the Fantom Opera Chain to create an immutable audit trail.
- Anyone will be able to verify that the data is authentic by scanning the label. The app will compare the current data to the data that exists on the blockchain.
These are the eleven data points stored on the blockchain for every single item:
- Product name
- Batch number
- Barcode number
- Expiry date
- Production date
- FDA number
- Producer’s name
- Location of scan
- Status of scan
- Time
- Date of scan
Why Fantom?
Fantom uses an innovative technology, Lachesis aBFT consensus, that allows ultra-fast confirmations. On Fantom, data becomes immutable and verifiable in seconds. The fast, scalable nature of Lachesis means that transaction fees can also be significantly lower than other networks.
The speed makes Fantom’s blockchain ideal for supply-chain tracking.
In comparison, if this program were Ethereum-based, pharmaceutical producers would have to wait at least 2 minutes to make sure that the data is immutable, and pay a hefty transaction fee for each item scanned.
The delay and the costs are so significant that the program would be unfeasible in the real world.
Additionally, if the network is bottlenecked with too many transactions, it may take hours or even days to confirm.
On Fantom, users won’t notice if they’re using a blockchain or not. And that should be the ultimate goal: replace the legacy technology with better technology.
What medical products will I be able to track?
Initially, Royal Star will distribute 50,000 Anti-bacterial Hand Sanitizers. Royal Start recently launched this product to fight COVID-19 in Afghanistan, and is endorsed by the World Health Organization.
Additionally, Royal Star will distribute tens of thousands of other medical products, including a pain reliever cream, cold&cough chewable tablets, and a Diacare foot cream.

What’s the goal?
This pilot program aims to demonstrate Fantom’s technology, its capability in supply chain management, to roll out the technology on a much larger scale throughout 2020 and significantly decrease the production and distribution of counterfeit medicines across the globe.